1. Introduction
With energy prices on the rise and solar technology becoming more accessible, more European homeowners and businesses are considering solar power. But before you invest in panels and batteries, there’s a critical decision to make: What type of solar system is right for you?
In 2025, the three most common configurations are:
- On-Grid (Grid-Tied) Solar Systems
- Off-Grid Solar Systems
- Hybrid Solar Systems
Each system offers different levels of energy independence, cost, complexity, and government incentives. This guide will help you understand the key differences, pros and cons, and choose the right option for your property, lifestyle, and energy goals.
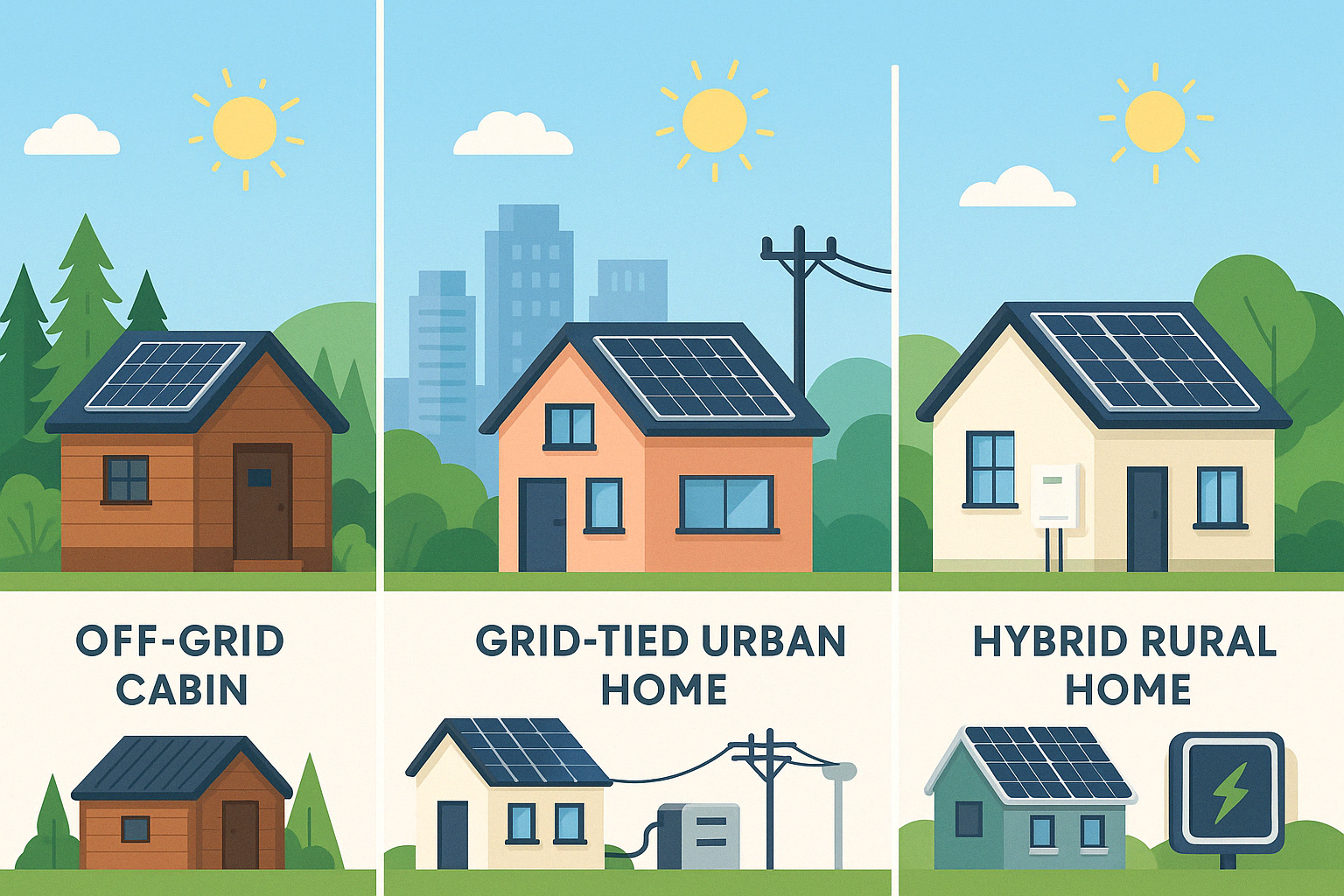
2. What Is an On-Grid Solar System?
An on-grid solar system (also called grid-tied) is connected directly to the public utility grid. During the day, your solar panels generate power that’s either used immediately in your home or fed into the grid.
✅ Key Features:
- No battery required
- Excess electricity exported to the grid
- Grid supplies power at night or during cloudy days
? Best For:
- Urban areas with stable grid access
- Homeowners looking to lower electricity bills
- Countries offering feed-in tariffs or net metering
⚠️ Drawbacks:
- No power during grid outages (unless paired with backup)
- Fully dependent on grid reliability
- Limited energy independence
In countries like Germany, on-grid systems are common due to favorable net-metering schemes and smart meter integration.
3. What Is an Off-Grid Solar System?
An off-grid system operates completely independently of the utility grid. All the energy you use must be generated and stored locally, typically through solar panels + battery + backup generator.
✅ Key Features:
- 100% energy independence
- Requires solar battery storage
- Often paired with diesel/gas backup generator
? Best For:
- Remote areas or rural homes
- Cabins, farms, or mobile homes
- Users wanting full grid independence
⚠️ Drawbacks:
- Higher upfront cost due to battery bank
- Energy use limited by storage capacity
- Requires careful sizing & design
Off-grid systems are gaining popularity in off-the-beaten-path areas of Spain, Greece, and the Alps where grid connection is expensive or unreliable.
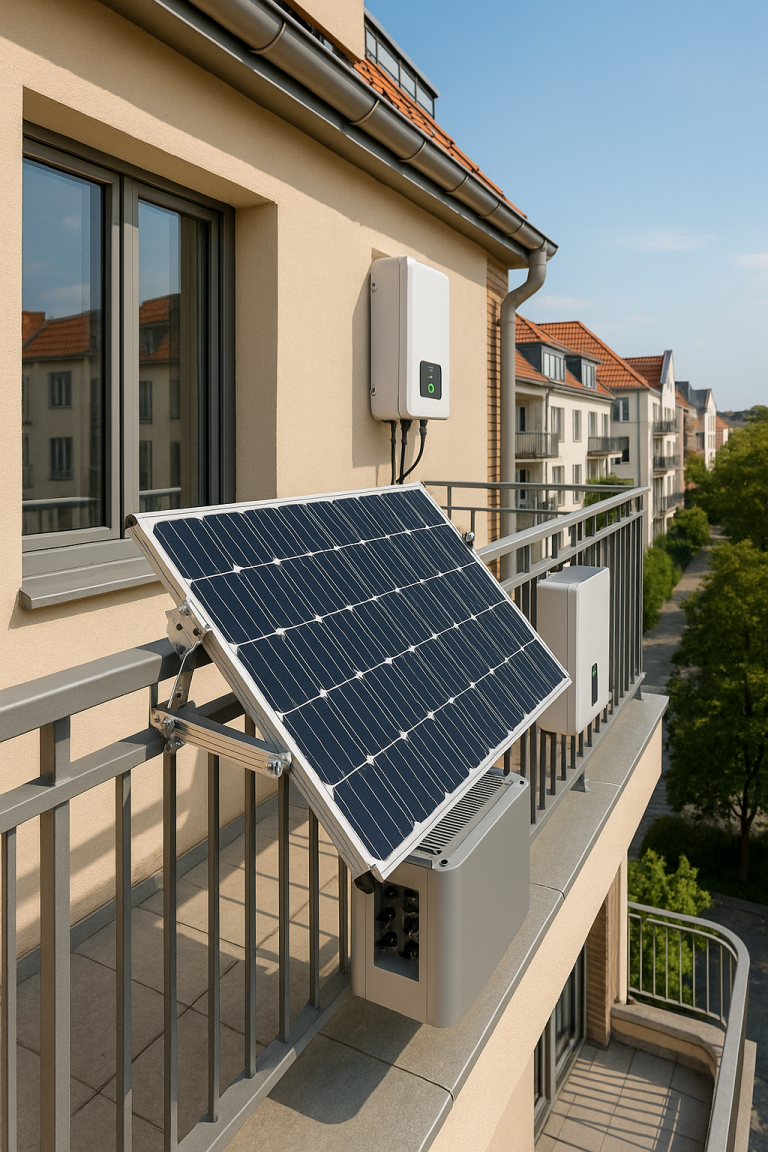
4. What Is a Hybrid Solar System?
A hybrid solar system combines the best of both worlds. It connects to the grid but also includes battery storage. It allows you to use solar energy, store excess in batteries, and draw from the grid as backup when needed.
✅ Key Features:
- Uses solar, battery, and grid power together
- Can operate during grid outages
- Smart inverters manage energy flow
? Best For:
- Semi-urban homes with frequent power cuts
- Smart homes seeking optimal self-consumption
- Businesses balancing energy cost & reliability
⚠️ Drawbacks:
- More expensive than simple grid-tied systems
- Requires smart inverter and BMS
- May have complex installation depending on system size
In 2025, many EU countries are offering subsidies for hybrid-ready homes and encouraging energy storage with PV.
5. Core Differences at a Glance
| Feature | On-Grid | Off-Grid | Hybrid |
| Grid Connection | Yes | No | Yes |
| Battery Storage | Optional | Required | Required |
| Works During Grid Outage | No | Yes | Yes |
| Setup Cost | Low | High | Medium to High |
| Energy Independence | Low | Full | Partial to High |
| Maintenance Complexity | Low | Medium | Medium to High |
6. Which Is Best Based on Your Lifestyle?
- Live in a city with stable grid? → On-grid system is cost-effective and low maintenance.
- Own a farm or mountain cabin? → Off-grid is your only option (with batteries + backup).
- Want to lower bills & have blackout protection? → Hybrid systems give flexibility and storage control.
- Operate a business with peak-hour loads? → Hybrid lets you time-shift usage and avoid high tariffs.
Remember: your ideal system depends on your goals, location, and power demand — not just budget.
7. Regulations & Incentives in Europe (2025 Update)
Europe in 2025 is actively encouraging solar adoption, but policies vary:
- ?? Germany: Incentives for battery storage and smart grid connection (KfW grants, MaStR registration required)
- ?? France: Self-consumption bonus (Prime à l’autoconsommation) + VAT reductions
- ?? Spain: 40–50% subsidies in some regions for solar + battery combos
- ?? Italy: Superbonus scheme includes hybrid & off-grid upgrades
- ?? Netherlands: Net metering being phased out → storage becoming essential
Hybrid systems often receive the most incentives, as they support grid stability and reduce peak demand.
8. Installation Requirements and Costs
| System Type | Typical Cost Range (EU) | Complexity |
| On-Grid | €4,000 – €8,000 | Low |
| Off-Grid | €9,000 – €20,000 | High |
| Hybrid | €8,000 – €15,000 | Medium |
Cost Factors:
- Battery size (kWh)
- Inverter type (hybrid inverter costs more)
- Mounting structure and cabling
- Smart controls (for hybrid automation)
Installation for hybrid/off-grid often requires professional planning, especially with 3-phase systems or multi-inverter setups.
9. System Expansion and Scalability
- On-Grid: Easy to add more panels, but limited without storage.
- Off-Grid: Must scale batteries and inverters in sync. Higher upfront.
- Hybrid: Modular. Easy to add more batteries, panels, or EV chargers.
Tip: Choose systems with stackable batteries, modular inverters, and smart BMS for future-proofing.
10. Conclusion – Which Should You Choose in 2025?
Let’s summarize:
✅ Choose On-Grid if:
- You want fast ROI and lower monthly bills
- You live in a well-connected area
- You’re eligible for net metering
✅ Choose Off-Grid if:
- You’re far from the grid
- You want total independence
- You’re ready for a higher investment
✅ Choose Hybrid if:
- You want the flexibility of battery storage + grid backup
- You’re planning for EV charging or time-of-use tariffs
- You want to future-proof your energy independence
In 2025, hybrid systems are becoming the go-to choice for homeowners across Europe — striking the best balance between reliability, autonomy, and cost savings.