Customer Profile
• ? Name: Johan Nilsson
• ? Location: Luleå, Sweden (65°N latitude)
• ? House: 180m² detached home
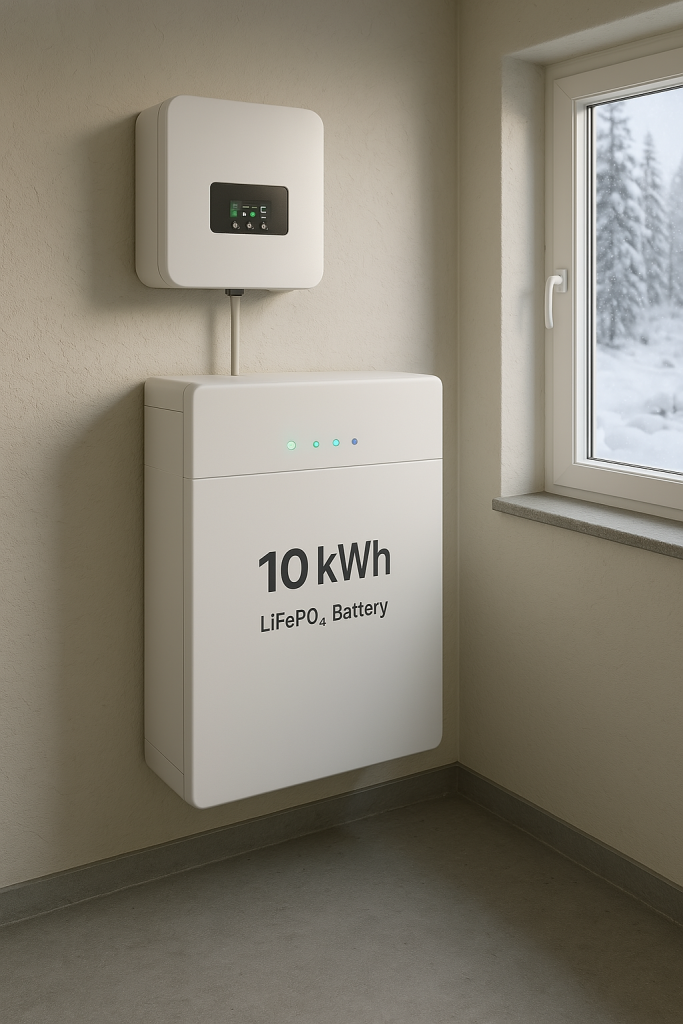
• ⚡ System: 6.2kW solar + 10kWh LiFePO₄ battery backup
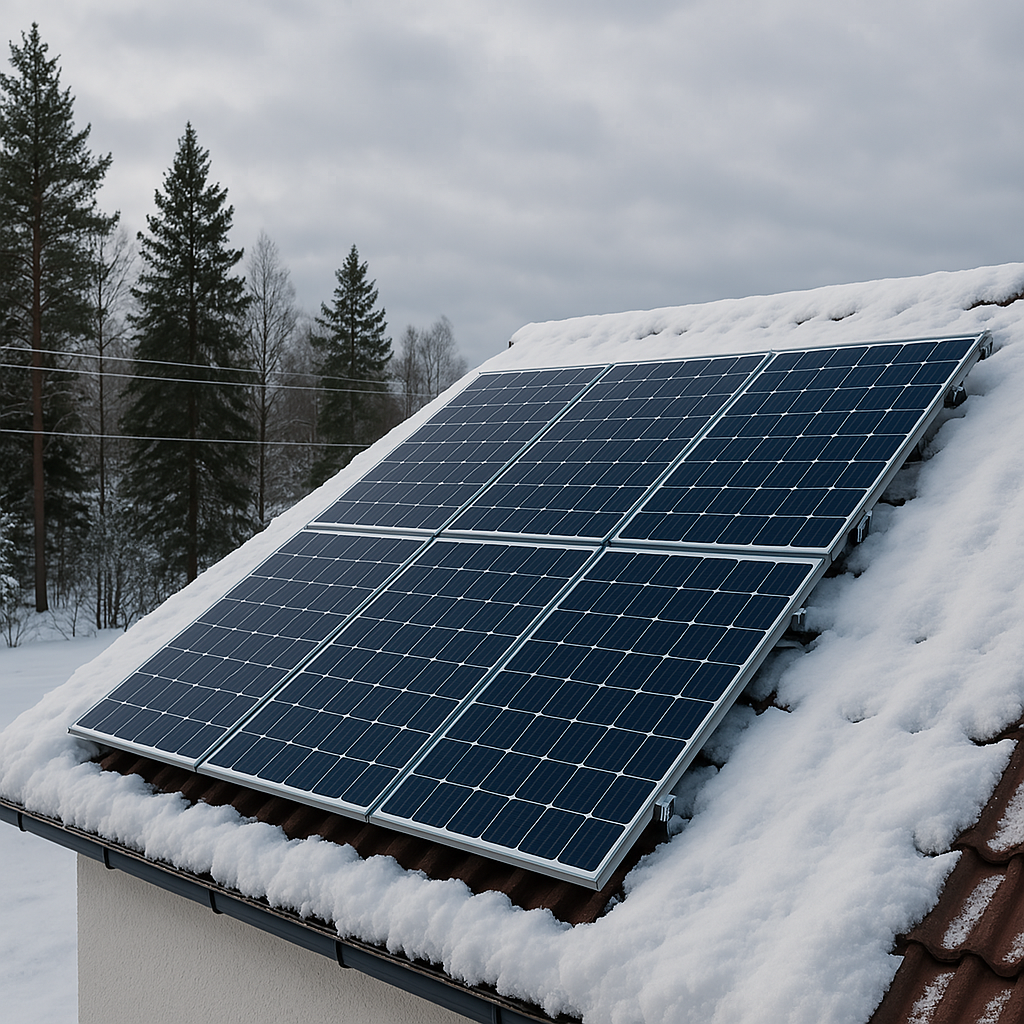
• ❄️ Climate: -25°C in winter, +27°C in summer, snow > 150 days/year
Johan wanted to reduce dependence on the regional grid and offset rising electricity costs. But the biggest concern? Snow and darkness in winter.

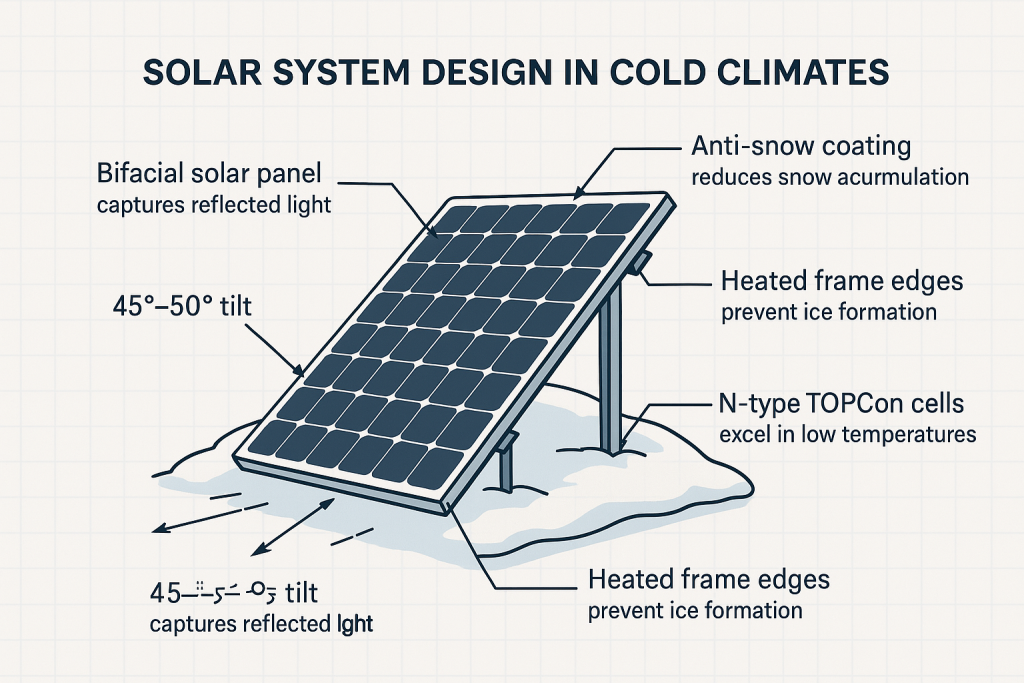
System Design Considerations
To deal with Luleå’s climate, Johan’s installer made several critical adaptations:
1. High Tilt Angle (45°–50°)
Steeper panels help snow slide off faster and capture low winter sun angles.
2. Bifacial Panels
These panels absorb sunlight from both sides, which helps when snow reflects light from below.
3. Anti-Snow Coating + Heated Frame
An anti-ice coating and low-voltage frame heaters help reduce snow accumulation.
4. N-Type TOPCon Technology
Better performance in low-light and cold conditions, with less degradation over time.
Performance Results After 12 Months
| Season | Avg. Daily Output | % of Expected Yield | Key Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Summer | 28–32 kWh | 102% | Excellent due to 20+ sunlight hrs |
| Winter | 4–8 kWh | 65–70% | Lower, but consistent |
| Annual Total | ~8,500 kWh/year | 94% of expected | Very good for this region |
Despite long winters, the system achieved 94% of its annual target output — far better than initially projected.
Customer Feedback
“I was skeptical at first, but the results speak for themselves. The system worked even during snowy weeks. Plus, the battery backup saved us during two power cuts.”
— Johan Nilsson

Lessons for Installations in Extreme Climates
1. Design is everything – Angle, technology, and panel type matter more than brand.
2. Maintenance access – Allow space to clear snow when needed.
3. Choose right batteries – Cold-resistant batteries like LiFePO₄ outperform others.
4. Data matters – Use apps to monitor performance in real time.

Conclusion: Solar Works Even in the Coldest Places
This case proves that solar panels can thrive even in harsh climates with proper system design. Technology like bifacial panels, N-type cells, and intelligent energy storage has made solar viable for more regions than ever before.




